⏪Previous Next⏩
In computer programming, an operator is a symbol with a special meaning, which is used to carry out a particular operation.
Operators behave similar to functions, in that they take an input and produce an output, but they differ syntactally to functions. For example, in
1 + 1, the plus sign (+) is an operator that adds the number on its left with the number on its right.
Python includes operators in the following categories:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison (Relational) Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Ternary (Conditional) Operator
These are explained below.
Arithmetic Operators
- + (addition)
- Returns the sum of two expressions.
- - (subtraction)
- Returns the difference of two expressions.
- * (multiplication)
- Returns the product of two expressions.
- ** (power)
- Returns the value of a numeric expression raised to a specified power.
- / (division)
- Returns the quotient of two expressions.
- // (floor division)
- Returns the integral part of the quotient.
- % (modulus)
- Returns the decimal part (remainder) of the quotient.
- Here's the result of applying each of the arithmetic operators to the same operands:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
print(500 + 20) print(500 - 20) print(500 * 20) print(500 / 20) print(500 // 20) print(500 % 20) print(20 ** 50)
- Output :
-
Relational Operators
- == (equal)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether two expressions are equal.
- != (not equal)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether two expressions are not equal.
- > (greater than)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether one expression is greater than the other.
- >= (greater than or equal)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether one expression is greater than or equal the other.
- < (less than)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether one expression is less than the other.
- <= (less than or equal)
- Returns a Boolean stating whether one expression is less than or equal the other.
1 2
print(1==1) print(1==2)
- Output:
-
Logical Operators
- and
- Returns the first operand that evaluates to False or the last one if all are True.
- or
- Returns the first operand that evaluates to True or the last one if all are False.
- not
- Returns a boolean that is the reverse of the logical state of an expression.
1 2
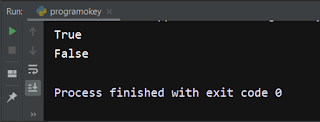
print(1==1 and 2==2) print(1==1 and 1==2)
- Output :
-
-
Assignment Operators
- = (simple assignment)
- Assigns a value to a variable(s).
- += (increment assignment)
- Adds a value and the variable and assigns the result to that variable.
- -= (decrement assignment)
- Subtracts a value from the variable and assigns the result to that variable.
- *= (multiplication assignment)
- Multiplies the variable by a value and assigns the result to that variable.
- /= (division assignment)
- Divides the variable by a value and assigns the result to that variable.
- **= (power assignment)
- Raises the variable to a specified power and assigns the result to the variable.
- %= (modulus assignment)
- Computes the modulus of the variable and a value and assigns the result to that variable.
- //= (floor division assignment)
- Floor divides the variable by a value and assigns the result to that variable.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
a = 10 b = 20 a = a + b print(a) a = 10 b = 20 a += b print(a)
- Output :
-
Bitwise Operators
- & (bitwise AND)
- Returns the result of bitwise AND of two integers.
- | (bitwise OR)
- Returns the result of bitwise OR of two integers.
- ^ (bitwise XOR)
- Returns the result of bitwise XOR of two integers.
- << (left shift)
- Shifts the bits of the first operand left by the specified number of bits.
- >> (right shift)
- Shifts the bits of the first operand right by the specified number of bits.
- ~ (bitwise complement)
- Sets the 1 bits to 0 and 1 to 0 and then adds 1.
1 2
print(500 | 200) print(500 & 200 )
- Output :
-
Conditional Operator
- if else
- Returns either value depending on the result of a Boolean expression.
1 2
a = 7 print("Low" if a < 10 else "High")
- Output :
-
Identity
- is
- Returns a Boolean stating whether two objects are the same.
Membership
- in
- Returns a Boolean stating whether the object is in the container.
















0 Comments