⏪Previous Next⏩
The list of various disks scheduling algorithm is given below. Each algorithm is carrying some advantages and disadvantages. The limitation of each algorithm leads to the evolution of a new algorithm.
- FCFS scheduling algorithm
- SSTF (shortest seek time first) algorithm
- SCAN scheduling
- C-SCAN scheduling
- LOOK Scheduling
- C-LOOK scheduling
- FCFS: FCFS is the simplest of all the Disk Scheduling Algorithms. In FCFS, the requests are addressed in the order they arrive in the disk queue.
Example
Consider the following disk request sequence for a disk with 100 tracks 45, 21, 67, 90, 4, 50, 89, 52, 61, 87, 25
Head pointer starting at 50 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using FCFS scheduling.
Number of cylinders moved by the head
= (50-45)+(45-21)+(67-21)+(90-67)+(90-4)+(50-4)+(89-50)+(61-52)+(87-61)+(87-25)
= 5 + 24 + 46 + 23 + 86 + 46 + 49 + 9 + 26 + 62
= 376
Advantages:
- Every request gets a fair chance
- No indefinite postponement
Disadvantages:
- Does not try to optimize seek time
- May not provide the best possible service
- SSTF: In SSTF (Shortest Seek Time First), requests having shortest seek time are executed first. So, the seek time of every request is calculated in advance in the queue and then they are scheduled according to their calculated seek time. As a result, the request near the disk arm will get executed first. SSTF is certainly an improvement over FCFS as it decreases the average response time and increases the throughput of system.
Example
Consider a disk queue with requests for I/O to blocks on cylinders
98, 183, 41, 122, 14, 124, 65, 67.
The SSTF scheduling algorithm is used.
The head is initially at cylinder number 53 moving towards larger cylinder numbers on its servicing pass.
98, 183, 41, 122, 14, 124, 65, 67.
The SSTF scheduling algorithm is used.
The head is initially at cylinder number 53 moving towards larger cylinder numbers on its servicing pass.
Total head movements incurred while servicing these requests
= (65 – 53) + (67 – 65) + (67 – 41) + (41 – 14) + (98 – 14) + (122 – 98) + (124 – 122) + (183 – 124)
= 12 + 2 + 26 + 27 + 84 + 24 + 2 + 59
= 236
Advantages:
- Average Response Time decreases
- Throughput increases
Disadvantages:
- Overhead to calculate seek time in advance
- Can cause Starvation for a request if it has higher seek time as compared to incoming requests
- High variance of response time as SSTF favours only some requests
- SCAN: In SCAN algorithm the disk arm moves into a particular direction and services the requests coming in its path and after reaching the end of disk, it reverses its direction and again services the request arriving in its path. So, this algorithm works as an elevator and hence also known as elevator algorithm. As a result, the requests at the midrange are serviced more and those arriving behind the disk arm will have to wait.
Example
Consider the following disk request sequence for a disk with 100 tracks
98, 137, 122, 183, 14, 133, 65, 78
Head pointer starting at 54 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using SCAN scheduling.
Number of Cylinders = 40 + 14 + 65 + 13 + 20 + 24 + 11 + 4 + 46 = 237
Advantages:
- High throughput
- Low variance of response time
- Average response time
Disadvantages:
- Long waiting time for requests for locations just visited by disk arm
- CSCAN: In SCAN algorithm, the disk arm again scans the path that has been scanned, after reversing its direction. So, it may be possible that too many requests are waiting at the other end or there may be zero or few requests pending at the scanned area.
Example
Consider the following disk request sequence for a disk with 100 tracks
98, 137, 122, 183, 14, 133, 65, 78
Head pointer starting at 54 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using C-SCAN scheduling.
No. of cylinders crossed = 40 + 14 + 199 + 16 + 46 + 4 + 11 + 24 + 20 + 13 = 387
These situations are avoided in CSCAN algorithm in which the disk arm instead of reversing its direction goes to the other end of the disk and starts servicing the requests from there. So, the disk arm moves in a circular fashion and this algorithm is also similar to SCAN algorithm and hence it is known as C-SCAN (Circular SCAN).
Advantages:
- Provides more uniform wait time compared to SCAN
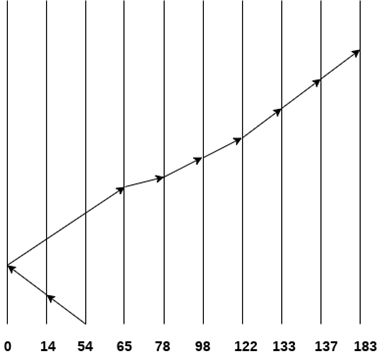
- LOOK: It is similar to the SCAN disk scheduling algorithm except for the difference that the disk arm in spite of going to the end of the disk goes only to the last request to be serviced in front of the head and then reverses its direction from there only. Thus it prevents the extra delay which occurred due to unnecessary traversal to the end of the disk.
Consider the following disk request sequence for a disk with 100 tracks
98, 137, 122, 183, 14, 133, 65, 78
Head pointer starting at 54 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using LOOK scheduling
Head pointer starting at 54 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using LOOK scheduling
Number of cylinders crossed = 40 + 51 + 13 + +20 + 24 + 11 + 4 + 46 = 209
- CLOOK: As LOOK is similar to SCAN algorithm, in similar way, CLOOK is similar to CSCAN disk scheduling algorithm. In CLOOK, the disk arm in spite of going to the end goes only to the last request to be serviced in front of the head and then from there goes to the other end’s last request. Thus, it also prevents the extra delay which occurred due to unnecessary traversal to the end of the disk.
Example
Consider the following disk request sequence for a disk with 100 tracks
98, 137, 122, 183, 14, 133, 65, 78
Head pointer starting at 54 and moving in left direction. Find the number of head movements in cylinders using C LOOK scheduling.
Number of cylinders crossed = 11 + 13 + 20 + 24 + 11 + 4 + 46 + 169 = 298
⏪Previous Next⏩
- What is an Operating System ?
- Discuss the structure off OS ?
- Explain type of OS?
- Explain Function of OS?
- Explain OS Services ?
- What do mean by system call ?List different type ofsystem call available ?
- what is process ? and Characteristics ?
- What is different process state? explain the same in details?
- write short note on user level and kernal level threads?
- explain what is thread and its type ?
- explain scheduler ? (short term,medium term,and long term)
- state and explain scheduling criteria ?
- Explain scheduling algorithm ? [ FCFS,SJF,PRIORITY,ROUND ROBINE.]
- What is process synchronization ? explain critical section problem and race condition ?
- what is Race Condition ?
- what is critical section problem?
- explain classical problem of synchronization?
- explain bounded - buffer problem?
- explain reader - writer problem ?
- explain Dining Philosophers Problem ?
- explain semaphores ? its type ?
- What is deadlock ?
- What are the 4 condition to produce deadlock ?
- explain methods of handling deadlock ?
- explain in detail deadlock prevention ?
- write short note on deadlock avoidance ?
- explain deadlock detection ?
- explain Banker algorithm with example ?
- What are memory management ?
- what is contiguous memory allocation and non - contiguous memory allocation ?
- explain concept of paging with neat diagram?
- differentiate contiguous and non - contiguous memory allocation ?
- explain in details various partitioning memory management?
- explain the concept of Segmentation ?
- what is Thrashing explain in details ?















0 Comments